Peroneal tendonitis is a common condition that affects the tendons on the outside of the ankle, and it can cause significant pain and discomfort. This condition can be caused by a variety of factors, including overuse, improper footwear, and high-impact sports. It is essential to receive prompt and appropriate treatment for peroneal tendonitis to avoid complications like chronic ankle instability and peroneal tendon tear.
In this article, we will discuss everything you need to know about peroneal tendonitis. Including its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, prevention, and related conditions. Whether you are a professional athlete or a casual jogger, this guide will help you understand how to treat and prevent peroneal tendonitis.
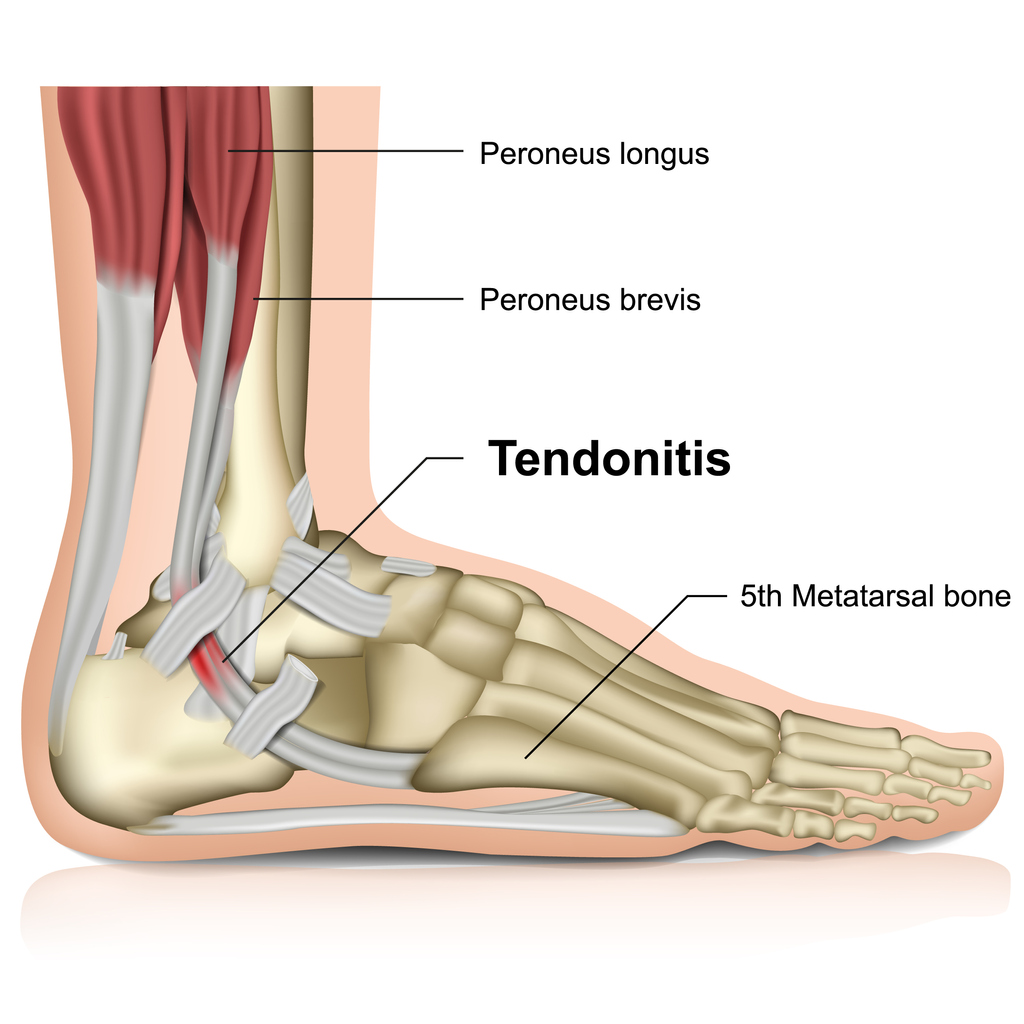
What is Peroneal Tendonitis?
Peroneal tendonitis is an inflammation or irritation of the peroneal tendons, which run along the outside of the ankle and connect to the muscles in the lower leg. These tendons are responsible for stabilizing the ankle joint and helping to turn the foot outward.
The most common cause of peroneal tendonitis is overuse, which can occur in athletes who participate in high-impact sports like running, basketball, and soccer. Repetitive stress on the tendons can cause small tears or inflammation, leading to pain and discomfort.
Other risk factors for peroneal tendonitis include improper footwear, ankle instability, and biomechanical abnormalities like flat feet or high arches. In some cases, peroneal tendonitis may occur after an ankle sprain or other ankle injury.
Symptoms of peroneal tendonitis include pain on the outside of the ankle, swelling, tenderness, and weakness in the ankle or foot. The pain may be worse during physical activity or when walking on uneven surfaces. In chronic cases, the ankle may become unstable, making it difficult to walk or participate in sports.
Diagnosis: How Do I Know if I Have Peroneal Tendonitis?
If you suspect that you have peroneal tendonitis, it is essential to see a doctor for a proper diagnosis. The diagnostic process usually begins with a physical exam. This entails a doctor will check for swelling, tenderness, and weakness in the ankle and foot.
Imaging tests like X-rays, ultrasound, or MRI may also be used to confirm the diagnosis and rule out other conditions like ankle sprains or stress fractures. X-rays can help identify any bone abnormalities that may be contributing to the problem. Ultrasound and MRI can provide detailed images of the soft tissues. This will allow the doctor to see any inflammation or tears in the peroneal tendons.
What are My Treatment Options for Peroneal Tendonitis
The treatment for peroneal tendonitis depends on the severity of the condition. In mild cases, conservative treatments like rest, ice, compression, and elevation may be sufficient to reduce inflammation and relieve pain. Physical therapy and stretching exercises may also help improve the strength and flexibility of the ankle and foot.
Regenerative medicine, such as platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy, can help treat peroneal tendonitis by promoting tissue repair and reducing inflammation. During PRP therapy, the patient’s own blood is drawn and processed to concentrate the platelets, which are then injected into the affected area to stimulate healing. This approach can provide an effective alternative to surgery and other traditional treatments.
In more severe cases, medications like nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or corticosteroid injections may be used to reduce pain and inflammation. Orthotics like ankle braces or shoe inserts may also help stabilize the ankle and reduce stress on the peroneal tendons.
In rare cases, surgery may be necessary to repair or remove damaged tissue in the peroneal tendons. Surgery is usually only recommended for severe cases or when conservative treatments have failed.
How to Prevent Peroneal Tendonitis Injuries
Preventing peroneal tendonitis is essential for anyone who participates in high-impact sports or activities that put stress on the ankle and foot. The following strategies can help prevent this condition:
- Wear proper footwear: Choose shoes with good arch support and cushioning to reduce stress on the peroneal tendons.
- Warm-up and cool-down: Always warm up before exercise or sports and cool down afterward. This helps to prepare the muscles and tendons for activity and reduce the risk of injury.
- Gradual progression: Gradually increase the intensity and duration of your physical activity to allow your body to adapt to the increased stress on the tendons.
- Strengthening exercises: Incorporate exercises that strengthen the ankle and foot muscles, including the peroneal tendons, into your fitness routine. This can help improve the stability of the ankle joint and reduce the risk of injury.
- Stretching exercises: Stretching exercises can help improve the flexibility of the ankle and foot and reduce the risk of injury. Focus on stretching the calf muscles, Achilles tendon, and peroneal tendons.
- Proper technique: Use proper technique when performing physical activities like running or jumping. Improper technique can put undue stress on the tendons and increase the risk of injury.
- Cross-training: Incorporate cross-training into your fitness routine to reduce the stress on the peroneal tendons. Alternating high-impact activities like running with lower-impact activities like cycling or swimming can help reduce the risk of injury.
Related Conditions
Peroneal tendonitis is closely related to other conditions that affect the ankle and foot, including posterior tibial tendonitis, ankle instability, and peroneal tendon tear.
Posterior tibial tendonitis is a condition that affects the tendon that runs along the inside of the ankle. It can cause pain and weakness in the ankle and foot. Like peroneal tendonitis, posterior tibial tendonitis can be caused by overuse, improper footwear, and biomechanical abnormalities.
Ankle instability is a condition that occurs when the ligaments that support the ankle become stretched or torn, leading to chronic instability and weakness in the ankle joint. Ankle instability can be caused by repeated ankle sprains or other injuries to the ankle.
Peroneal tendon tear is a severe condition that occurs when the peroneal tendons become completely torn, leading to significant pain and instability in the ankle and foot. Peroneal tendon tears are usually caused by acute trauma or repetitive stress on the tendons over time.
Summary
This ankle injury can be a debilitating condition that affects the ankle and foot, but it is treatable and preventable with the right approach. If you suspect that you have peroneal tendonitis, seek medical attention promptly to receive an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Remember, peroneal tendonitis is closely related to other conditions like posterior tibial tendonitis, ankle instability, and peroneal tendon tears. Be aware of the signs and symptoms of these conditions and seek medical attention if you experience any pain or discomfort in the ankle or foot.
With the right gameplan, you can manage and prevent peroneal tendonitis and enjoy a healthy and active lifestyle.
Learn More About Alternative Ways to Alleviate Your Pain
Get back to doing the things you love, faster & without surgery.
Request an Appointment Today!