Body MRI
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a non-invasive medical test that provides detailed pictures of the inside of the body through the use of magnetic fields, radio waves, and a computer. The primary purpose of this procedure is to assist in the diagnosis or monitoring of health conditions. Sometimes, pregnant women utilize MRI’s to monitor the baby. Before doing a MRI test, make sure you tell your doctor about your medical history. Although the magnetic field isn’t dangerous, it can cause some medical devices to malfunction, so it’s important you tell the doctor if you have any sort of device or metal inside your body.
Common Uses of a Body MRI
MRI imaging typically analyzes:
- Chest / Abdominal Organs (kidneys, liver, adrenal glands, spleen, etc)
- Blood Vessels
- Pelvic Organs (bladder, ovaries, uterus, reproductive organs, etc)
- Lymph Nodes
More specifically, this test allows physicians to diagnose and/or monitor treatment for certain conditions including:
- Chest, Abdominal, or Pelvic Tumor
- A fetus in the womb
- Heart problems
- Liver Diseases
- Inflammation of the Vessels
Preparation
You can first expect to change into a hospital gown before an MRI in order to prevent unnecessary objects appearing in the images. Generally speaking, you should be able to eat, drink, and take any medications as normal before the procedure unless you hear otherwise from the doctor.
If you are pregnant, don’t hesitate to tell your doctor. Despite not having any harmful effects on pregnant women or their babies, both individuals are still in a strong magnetic field and should not risk having an MRI under those conditions.
Additionally, if you’re someone who has a fear of small enclosed spaces (claustrophobia), then ask your doctor to prescribe you a mild sedative before your exam.
Before entering the exam room, make sure you remove all jewelry and accessories, or just leave them at home.
- Jewelry, watches, hearing aids, credit cards
- Metal zippers, hairpins
- Removable dental work
- Pocket Knives, eyeglasses, pens
- Body piercings
- Phones or other mobile devices
Items like these can interfere with the magnetic field and potentially cause burns.
Potential Barriers
Metal implants are usually acceptable for an MRI exam, though there are a few that may not be safe, such as:
- Ear implants
- Metal coils
- Cardiac Defibrillators
- Brain aneurysm clips
- Vagal nerve stimulators
If you have any medical devices inside your body, then tell your doctor immediately, as they can pose a risk. Implanted devices usually have a pamphlet explaining the MRI risks for that particular device. If you have this pamphlet, we recommend bringing it to your exam for documentation & safety purposes. For some reason if you aren’t sure or if there’s any question from doctors, then you can get an x-ray to detect & identify any metal objects.
Dyes in tattoos could contain iron and heat up during an MRI scan, but this is rare. You shouldn’t have to worry about the magnetic field affecting braces, tooth fillings, or cosmetics, other than the fact that they could potentially distort facial images. Let your technologist know if any of these apply to you.
Children may require anesthesia or sedation in order to complete an MRI without moving, but this depends on their age and the type of exam. In the initial exam, you will be told how to prepare the child. If you would rather not sedate your child, there are some clinics who have professionals work with children and essentially prepare them for the MRI to relieve anxiety. Depending on the facility, they may even offer goggles for the child so they can watch a movie during the exam & stay still for the images.
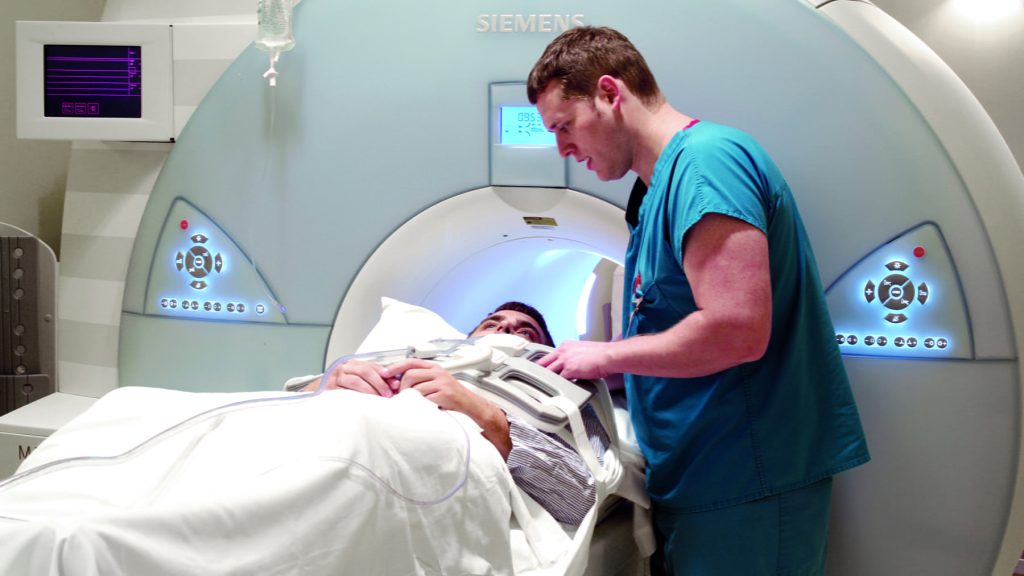
Equipment
An MRI machine is a large cylinder-shaped tube surrounded by a magnet. Your role is to lie on a table that slides into a “tunnel” like space in the center of the magnet. There are different types of MRI units such as short-bore systems, which are specifically designed to restrict the magnet from completely surrounding you. Similarly, an “open” MRI is open on its’ sides, which is helpful for bigger patients and those who are claustrophobic. They produce very high quality images for a variety of exams.
 Source
Source
Procedure Information
How it works
Body MRI’s do not use radiation like x-rays and CT exams. Instead, they use radio waves that re-aligns hydrogen atoms that are naturally existent in the body. As the realignment occurs, energy emits, which in turn produces a picture. Usually, the magnetic field in MRI units is created by an electric current passing through wire coils. These coils are important because they are responsible for sending and receiving radio waves, along with producing signals. Don’t let this intimidate you, as this electric current does not come in contact with the patient.
Once these signals occur, the computer creates a series of images that portrays the inside of the body. As opposed to x-rays and CT scans, MRI’s typically have a stronger ability to distinguish diseased vs normal tissue.
How it’s performed
To begin the body MRI process, the technologist will place you on a movable exam table and position you accordingly, which may involve using straps to help you stay still. Afterwards, they might set coil devices next to your body to promote sending & receiving of radio waves. The exams generally utilize multiple runs which could last several minutes and create different noises. Once you are inside the magnet of the unit, the technologist will examine you outside of the room, and you can communicate with them through an intercom. Overall, this process should take about 30-50 minutes.
What to expect during and after
There should not be any pain during or after this procedure. Some people get a little anxious due to being “closed-in” in a small area with the loud scanner, but that’s the only potential discomfort. In addition to this, the examine areas of your body may feel warm, which is perfectly normal. However, if it bothers you at all, then don’t hesitate to tell the technologist. You just want to make sure that you are staying as still as possible while the images generate, which only takes a few seconds per image.
When you hear and / or feel a noisy thumping sensation, then that means the pictures are being taken. Most patients (including young children) will be given headphones for the exam to limit the noise. Generally, the scanners contain air-condition and are fairly light. If you aren’t sedated, then you can resume usual everyday activities without restrictions after your MRI exam.
Results
The doctor who conducted your exam will analyze & interpret your MRI images and send a signed report directly to your primary care physician. Once your PCP receives the data, he/she will share it with you. Then, your doctor may schedule a follow-up exam depending on the case. For instance, any potential issues may require further evaluation, or your doctor may want to see if your prescribed treatment is working
Benefits vs Risks
Benefits
- Non-invasive
- No radiation exposure
- Proven valuableness in diagnosing certain conditions
- Accurate diagnosis of diseases
- Detects abnormalities
- No contrast injection
Risks
- Little-to-no risk
- If sedation is used, it’s possible to use too much. However, vital signs will monitor this.
- Magnetic field can cause implanted medical devices to malfunction
- Allergic reaction risk if exam utilizes contrast material
Limitations
Weight: Larger patients may have trouble fitting into some body MRI machines, as there are weight limits.
Implants: Any metallic objects, such as implants, can cause image distortion.
Quality of Images: There are many factors that contribute to the distortion of MRI images. Since the exam requires full stillness and breath-holding, it can be challenging. This is especially the case in such a confined space that tends to trigger mild anxiety. Even an irregular heartbeat could affect image quality.
Distinction: There are nit-picky things that the MRI can’t always distinguish – such as cancer tissue and edema fluid.
Cost & Time: MRI’s are a bit more lengthy in comparison to other imaging tests, and tend to cost more.
Learn More About Alternative Ways to Alleviate Your Pain
Get back to doing the things you love, faster & without surgery.
Request an Appointment Today!