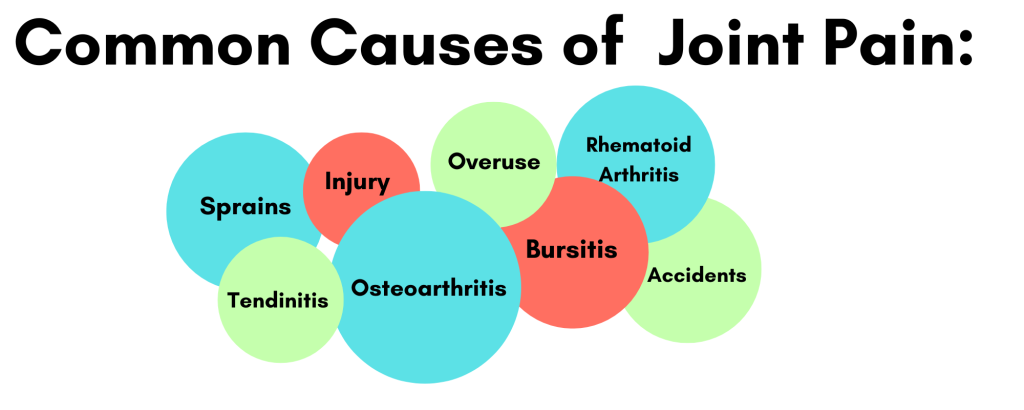
Joint pain is a common ailment affecting millions of people worldwide. Whether due to arthritis, injury, or other underlying conditions, finding effective treatments is crucial for maintaining a good quality of life. Here are five treatments that are commonly used to treat joint pain.
1. Over-the-Counter Pain Relievers:
Over-the-counter (OTC) pain medications, such as acetaminophen and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen and naproxen, are commonly used to manage joint pain. These medications help reduce inflammation and alleviate pain, making daily activities more comfortable for individuals suffering from conditions like arthritis or minor joint injuries. By blocking the production of certain chemicals in the body that cause pain and inflammation, OTC pain relievers can provide effective, temporary relief, allowing individuals to maintain their mobility and quality of life.
2. Corticosteroid Injections:
Corticosteroid injections are used to reduce inflammation and provide relief from severe joint pain. While they can be effective in the short term, repeated use of steroid injections can weaken tendons and ligaments, increasing the risk of injury. Frequent injections can also lead to joint degradation and may even accelerate the progression of arthritis.
3. Immobilization and Rest:
Rest and immobilization are essential strategies for managing joint pain, particularly following an injury or during flare-ups of chronic conditions like arthritis. Resting the affected joint helps to reduce stress and prevent further damage, allowing the body to initiate the healing process. Immobilization, often achieved through the use of splints, braces, or slings, restricts movement and stabilizes the joint, which can decrease inflammation and pain. This approach not only promotes recovery but also prevents additional strain on the joint, facilitating a quicker and more effective healing period.
4. Heat Therapy:
Heat therapy is a popular and effective method for alleviating joint pain, particularly for chronic conditions like arthritis. Applying heat to the affected area helps to increase blood flow, relax muscles, and loosen stiff joints, which can significantly reduce discomfort and improve mobility. Methods of heat therapy include using warm towels, heating pads, or taking warm baths. The warmth helps to soothe the pain by dilating blood vessels, enhancing circulation, and promoting the delivery of oxygen and nutrients to the joints.
5. Dietary Supplements:
Dietary supplements are often used to manage joint pain, particularly in conditions like osteoarthritis. Supplements such as glucosamine, chondroitin, and omega-3 fatty acids are popular for their potential to reduce inflammation and support joint health. Glucosamine and chondroitin are thought to help maintain cartilage structure and slow its deterioration, while omega-3 fatty acids, commonly found in fish oil, have anti-inflammatory properties that can reduce joint stiffness and pain. Always consult with your doctor before starting or stopping a new supplement.
Joint Pain: Alternative Solutions
Managing joint pain effectively often requires a multifaceted approach. While common treatments like over-the-counter pain relievers, corticosteroid injections, immobilization, heat therapy, and dietary supplements have their place, there are other available treatments designed to give you long lasting effects. Here are some alternative treatments that address the root causes of joint pain and promote overall joint health.
1. Physical Therapy and Exercise:
One of the most effective ways to manage joint pain is through physical therapy and regular exercise. Physical therapists can design personalized exercise programs that strengthen the muscles around your joints, improve flexibility, and enhance overall mobility. Low-impact exercises such as swimming, cycling, and yoga can help keep joints flexible and reduce stiffness without causing additional strain. Consistent, guided movement can also help prevent muscle atrophy and improve joint stability.
2. Regenerative Medicine:
Regenerative medicine offers promising alternatives to traditional treatments. Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) therapy and MFAT (Stem cells) therapy are two options that use the body’s natural healing mechanisms to repair damaged tissues. PRP therapy involves injecting a concentration of the patient’s own platelets into the affected joint to promote healing and reduce inflammation. MFAT therapy, on the other hand, involves the use of stem cells to regenerate damaged joint tissues. Both treatments aim to improve joint function and reduce pain by addressing the underlying damage.
3. Chiropractic Care:
Chiropractic care involves the manipulation of the spine and other parts of the body to improve alignment and relieve pain. Chiropractic adjustments can help reduce pressure on joints, improve mobility, and enhance overall joint function. Regular chiropractic care can be an effective part of a comprehensive plan.
4. Diet and Nutrition:
A balanced diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods can play a crucial role in managing joint pain. Foods such as fatty fish (rich in omega-3 fatty acids), fruits, vegetables, nuts, and whole grains can help reduce inflammation and provide essential nutrients for joint health. Maintaining a healthy weight through proper nutrition also reduces the strain on weight-bearing joints, which can alleviate pain. Consulting with a nutritionist or dietitian can help you develop a dietary plan that supports joint health and overall well-being.
5. Massage Therapy:
Regular massage therapy can help reduce muscle tension, improve circulation, and promote relaxation. Massage can specifically target the muscles around the joints, helping to alleviate pain and improve mobility. Techniques such as Swedish massage, deep tissue massage, and trigger point therapy can be particularly beneficial.
Learn More About Alternative Ways to Alleviate Your Pain
Get back to doing the things you love, faster & without surgery.
Request an Appointment Today!
Sources:
Dietary Supplements as Disease-Modifying Treatments in Osteoarthritis: A Critical Appraisal. (n.d.-b). In National Library of Medicine. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4103717/