Hip labral tears can be debilitating, causing significant pain and limiting mobility. Traditional treatments, including physical therapy, medications, or even surgery, have varying degrees of success and come with their own set of challenges. However, recent advancements in regenerative medicine have opened up new possibilities for healing. One such promising treatment involves using adipose-derived stem cells (ADSCs) to repair damaged hip labral tissues.
Understanding Hip Labral Tears
The hip joint is a ball-and-socket joint that allows for a wide range of motion. The labrum is a ring of cartilage that surrounds the hip socket (acetabulum), providing stability and cushioning for the joint. A hip labral tear occurs when this cartilage is damaged, either from acute injury, repetitive motion, or structural abnormalities such as hip dysplasia or femoroacetabular impingement (FAI).
- Common symptoms of a hip labral tear include:
- A locking, clicking, or catching sensation in the hip join
- Groin or hip pain that worsens with activity.
- Stiffness and reduced range of motion.
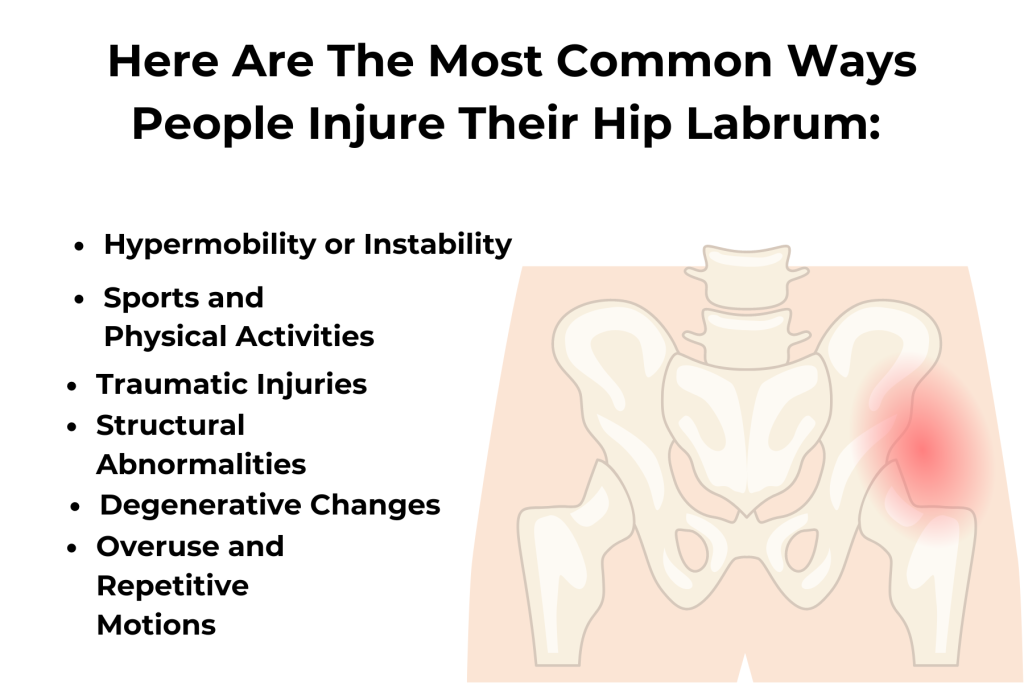
Current Treatments for Hip Labral Tears
Treatment options for hip labral tears typically begin with conservative methods, such as:
- Physical therapy
- Anti-inflammatory medications
- Corticosteroid injections.
These treatments aim to alleviate pain and improve function but may not fully address the underlying issue. In more severe cases, surgery may be required.
Arthroscopic surgery is the most common procedure, where the damaged labrum is either repaired or reconstructed using sutures. While surgery can be effective, it often comes with a lengthy recovery period and the risk of complications.
Adipose Stem Cells: What Are They?
Stem cells are unique cells with the ability to differentiate into various cell types and promote tissue repair. Adipose-derived stem cells (ADSCs) are a type of mesenchymal stem cell found in fat tissue. These cells have several advantages:
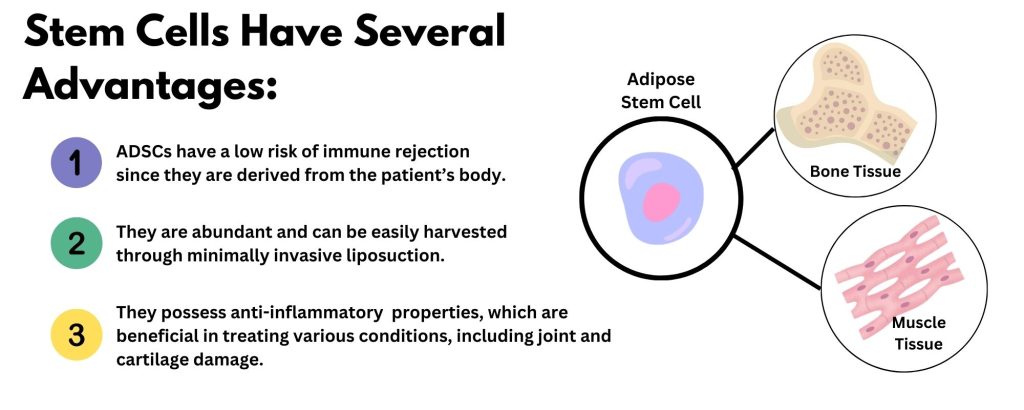
How Do They Work?
ADSCs promote healing by releasing growth factors and cytokines that reduce inflammation and stimulate the body’s natural repair mechanisms. When injected into damaged tissue, these cells can differentiate into various cell types, such as cartilage cells (chondrocytes), to repair and regenerate the labral tissue. This makes them particularly suited for treating hip labral tears, where cartilage damage is the primary concern.
Adipose Stem Cells in Treating Hip Labral Tears
ADSCs can help regenerate cartilage and reduce inflammation, effectively reducing pain and improving function in conditions like osteoarthritis and labral tears. Receiving ADSC injections for hip labral tears can lead to significant pain reduction and improved joint function.
Benefits of Using ADSCs Over Traditional Methods
Adipose-derived stem cell therapy offers several advantages over conventional treatments:
- Minimally Invasive: The procedure involves a simple liposuction to harvest stem cells, followed by an injection into the affected hip joint, eliminating the need for major surgery.
- Reduced Recovery Time: Patients can typically return to daily activities much sooner than after surgical interventions.
- Natural Healing: Unlike synthetic drugs or surgical implants, ADSCs promote the body’s natural healing process, potentially leading to more sustainable outcomes.
Hip Labrum Tear: The Adipose Stem Cell Therapy Process
How Are Adipose Stem Cells Harvested and Prepared?
The procedure for ADSC therapy involves several steps:
Preparation: The concentrated stem cells are then prepared for injection.
Harvesting: A small amount of fat tissue is extracted from the patient’s body, usually from the abdomen or thighs, using a minimally invasive liposuction procedure.
Isolation: The harvested fat is processed to isolate the stem cells. This typically involves centrifugation or enzymatic digestion to separate the ADSCs from other cellular components.
Administration and Post-Procedure Care:
The ADSCs are injected directly into the hip joint using ultrasound guidance to ensure precise placement. Following the injection, patients are advised to avoid strenuous activities for a few weeks, although light activities and physical therapy may be encouraged to promote recovery. Most patients experience minimal downtime and can return to their regular routines relatively quickly.
Could Adipose-Derived Stem Cells (ADSCs) Be an Alternative to Surgery for Hip Labral Tears?
Adipose-derived stem cells (ADSCs) are a promising alternative to surgery for treating hip labral tears. Surgery, while effective in some cases, carries several risks and challenges that ADSC therapy can potentially overcome. Here’s a closer look at why ADSCs may be a better option than traditional surgical approaches:
- Minimally Invasive: ADSC therapy involves a simple injection, unlike surgery, which requires incisions and repair work. This reduces trauma, risk of infection, and complications.
- Faster Recovery: Patients recover quicker with ADSCs, often returning to normal activities in days or weeks, while surgical recovery can take months and requires extensive rehabilitation.
- Natural Healing: ADSCs promote the body’s natural regeneration of labral tissue, potentially offering more sustainable and longer-lasting results than surgery.
- Less Pain and Discomfort: ADSC therapy typically results in less post-procedure pain and reduces the need for opioid pain management compared to surgery.
- Lower Risk of Repeat Procedures: Unlike surgery, which may require revisions or have long-term complications, ADSCs reduce the likelihood of needing additional treatments.
- Customized Treatment: ADSCs offer a personalized approach, using the patient’s own cells, which minimizes the risk of immune rejection and enhances healing.
Adipose-derived stem cell therapy provides a safer, quicker, and more natural alternative to surgery for treating hip labral tears, making it a compelling choice for patients seeking effective and less invasive solutions.
Learn More About Alternative Ways to Alleviate Your Pain
Get back to doing the things you love, faster & without surgery.
Request an Appointment Today!