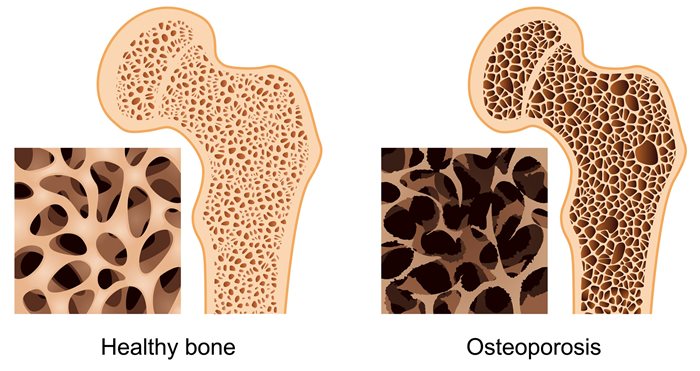
Osteoporosis is a prevalent skeletal disorder characterized by reduced bone density and increased bone fragility, leading to an elevated risk of fractures. With an aging population and a rise in sedentary lifestyles, the burden of osteoporosis has become a significant healthcare challenge. While current treatments focus on managing symptoms and slowing down bone loss, regenerative medicine holds tremendous potential to revolutionize the field by providing innovative therapeutic strategies that target the root causes of osteoporosis.
Understanding Osteoporosis: A Silent Threat
Osteoporosis is often referred to as a “silent disease” because it progresses silently, with no noticeable symptoms until a fracture occurs. The condition primarily affects postmenopausal women, but it can also affect men and younger individuals with certain risk factors. Osteoporosis occurs when the balance between bone formation and resorption is disrupted, leading to an overall decrease in bone mass and deterioration of bone microarchitecture.
Symptoms of Osteoporosis:
- Back pain, often due to a fractured or collapsed vertebra
- Loss of height over time
- Stooped posture or kyphosis
- Bones that fracture easily, even with minor falls or injuries
- Decreased bone density (often found on scans)
- Weak or brittle nails
- Reduced grip strength
- Joint or bone pain
- Difficulty with mobility and balance due to weakened bones
Current Treatment Approaches:
Traditional treatments for osteoporosis aim to slow down bone loss and reduce fracture risk. These include lifestyle modifications, dietary supplementation with calcium and vitamin D, exercise, and pharmacological interventions such as bisphosphonates, hormone replacement therapy, and selective estrogen receptor modulators. While these treatments can provide some benefits, they have limitations. Some individuals may not respond well to these interventions or may experience side effects.
Regenerative Medicine: The New Frontier
Regenerative medicine represents a paradigm shift in healthcare, focusing on harnessing the body’s natural healing mechanisms to restore damaged or diseased tissues. The field offers a promising array of innovative approaches for osteoporosis treatment.
Stem Cell Therapy
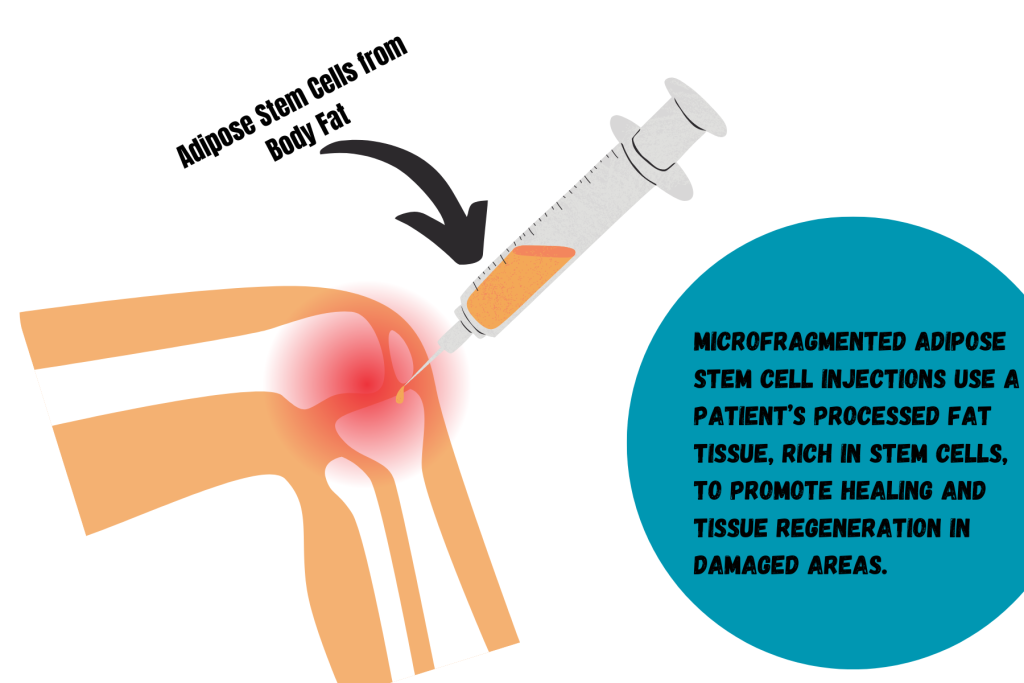
Stem cells possess the remarkable ability to differentiate into various cell types and promote tissue regeneration. Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), derived from sources such as bone marrow or adipose tissue, have shown promising results in preclinical and clinical studies for osteoporosis. These cells can differentiate into osteoblasts, the cells responsible for bone formation, and enhance bone regeneration and remodeling. Additionally, MSCs release paracrine factors that modulate the local environment, reduce inflammation, and promote the recruitment of endogenous stem cells.
Growth Factors and Cytokines
Regenerative medicine utilizes growth factors and cytokines to stimulate bone formation and enhance bone healing. For instance, bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs), which naturally occur in the body, have been extensively studied for their osteoinductive properties. These proteins can promote the differentiation of MSCs into osteoblasts and stimulate new bone formation. Other growth factors, such as platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) and insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1), have also demonstrated potential in promoting bone healing and regeneration.
Tissue Engineering and Biomaterials
Tissue engineering combines cells, biomaterial scaffolds, and growth factors to create functional tissue substitutes. In the context of osteoporosis, tissue engineering aims to develop scaffolds that mimic the natural bone structure and provide an environment conducive to bone regeneration. These scaffolds can be seeded with stem cells and loaded with growth factors to enhance bone formation. Advancements in 3D printing and biomaterial technology have facilitated the production of patient-specific scaffolds with precise architecture and mechanical properties, enhancing their regenerative potential.
Gene Therapy
Gene therapy holds promise for addressing the genetic factors associated with osteoporosis. By delivering therapeutic genes directly to bone cells, it is possible to enhance bone formation and inhibit bone resorption. For instance, the introduction of genes encoding bone morphogenetic proteins or osteogenic transcription factors can stimulate bone formation. Additionally, gene therapy can be used to inhibit the production of proteins involved in bone resorption, such as receptor activator of nuclear factor-kappa B ligand (RANKL).
Osteoporosis and Regenerative Medicine: Top 5 Frequently Asked Questions
What is osteoporosis, and what are its common symptoms? Osteoporosis is a condition where bones become weak and brittle, leading to symptoms like back pain, loss of height, and frequent fractures.
How is osteoporosis typically treated? Treatments include medications, calcium and vitamin D supplements, lifestyle changes, and physical therapy to strengthen bones and prevent fractures.
What is regenerative medicine, and can it help with osteoporosis? Regenerative medicine involves repairing or regenerating damaged tissues. For osteoporosis, it may use stem cells or other therapies to promote bone growth.
Are regenerative treatments for osteoporosis safe and effective? While promising, regenerative treatments are still being studied for safety and effectiveness. Consult with a specialist to understand potential benefits and risks.
Who is a candidate for regenerative treatments for osteoporosis? Candidacy depends on factors like the severity of osteoporosis and overall health. A consultation with a healthcare provider is needed to determine eligibility.
Learn More About Alternative Ways to Alleviate Your Pain
Get back to doing the things you love faster & without surgery.
Request an Appointment Today!