The incidence of a herniated disc is about 5 to 20 cases per 1000 adults annually. Hundreds of thousands of people suffer each year. A herniated disc is a condition that affects the spinal cord, causing significant pain and discomfort. This condition, also known as a slipped disc or bulging disc, is a common problem that affects millions of people worldwide. The symptoms of a herniated disc can range from mild to severe, and in some cases, it can cause debilitating pain that affects the quality of life.
While herniated discs can be treated with medication, physical therapy, and other non-surgical treatments, in some cases, surgery may be necessary. However, many people wonder if it is possible to avoid lumbar surgery with a herniated disc. In this blog post, we will explore the causes and symptoms of herniated discs, as well as the available treatment options. We will also discuss whether it is possible to avoid surgery with a herniated disc and what factors determine whether surgery is necessary.
What are Herniated Discs?
A herniated disc is a condition that occurs when the soft tissue between the vertebrae in the spine protrudes through a tear in the outer layer of the disc. This condition can occur in any part of the spine. But is most common in the lower back, or lumbar region.
The causes of herniated discs can vary, but they are often the result of age-related wear and tear on the spine. Other causes of herniated discs include injury, trauma, and poor posture.
Causes of Herniated Discs
A herniated disc, also known as a slipped or ruptured disc, occurs when the soft gel-like center of a spinal disc protrudes through a tear in the outer, fibrous layer. This can result in pressure on the nerves, leading to pain, weakness, and numbness in the affected area.
The most common cause of herniated discs is age-related wear and tear on the spinal discs. As people age, the discs lose their elasticity, become less flexible, and are more susceptible to injury. However, other factors such as trauma, repetitive strain, and genetics can also contribute to the development of herniated discs.
Certain lifestyle factors such as obesity, smoking, and a sedentary lifestyle can also increase the risk of developing herniated discs. Additionally, occupations that involve heavy lifting, bending, or twisting can put excessive stress on the spine and increase the risk of herniated discs.
It is important to take preventative measures such as maintaining a healthy weight, exercising regularly, practicing good posture, and avoiding activities that strain the back to reduce the risk of developing herniated discs.
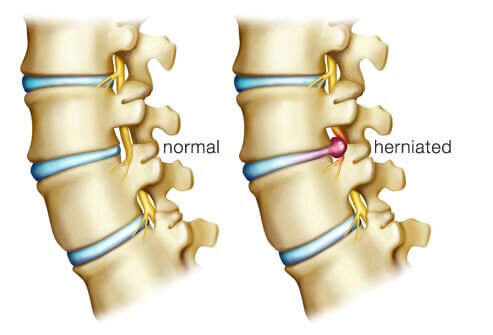
Symptoms of Herniated Discs
The symptoms of herniated discs can vary depending on the location of the disc and the severity of the condition. Common symptoms include:
- Pain in the back, legs, or arms
- Tingling or numbness in the affected area
- Muscle weakness
- Loss of sensation in the affected area
- Reduced range of motion
Types of Herniated Discs
There are different types of herniated discs, including slipped disc in back and bulging disc.
- Slipped Disc in Back: A slipped disc in the back occurs when the soft tissue between the vertebrae protrudes through a tear in the outer layer of the disc. This condition can cause pain and discomfort in the lower back.
- Bulging Disc: A bulging disc occurs when the soft tissue between the vertebrae protrudes outward, but the outer layer of the disc is not torn. This condition can cause mild to moderate pain and discomfort.
Herniated Disc Treatments
Non-Surgical Herniated Disc Options
The treatment for a herniated disc depends on the severity of the condition and the location of the disc. Non-surgical treatments are often used to manage mild to moderate herniated discs. These treatments include:
- Medication: Pain medication, muscle relaxants, and anti-inflammatory drugs can help manage the pain and discomfort associated with a herniated disc.
- Physical Therapy: Physical therapy can help improve strength and flexibility in the affected area. This can help reduce pain and improve range of motion.
- Chiropractic Care: Chiropractic care involves using manual manipulation to help reduce pain and improve range of motion in the affected area.
- PRP Injections
- Prolotherapy
- Stem Cells
Regenerative Medicine for Herniated Discs
Platelet-rich plasma (PRP), prolotherapy, and regenerative medicine are emerging as promising alternatives to surgery for herniated discs. These therapies aim to promote the natural healing process of the body and can be a safe and effective treatment option for many patients.
PRP involves injecting a concentrated solution of the patient’s own platelets, which contain growth factors, into the affected area. This promotes tissue regeneration, reducing inflammation and pain, and promoting healing.
Prolotherapy involves injecting a solution of dextrose and other substances into the affected area to stimulate the growth of new tissue and strengthen weakened ligaments and tendons. This can help reduce pain and improve mobility.
Regenerative medicine involves using stem cells or growth factors to promote tissue regeneration and healing. This can be done through injection or other techniques, depending on the individual case.
These therapies are less invasive than surgery and have a shorter recovery time. They also have fewer risks and complications associated with them. It is important to discuss with your healthcare provider if PRP, prolotherapy, or regenerative medicine is a suitable treatment option for your specific case of herniated discs.
Surgical Herniated Disc Treatments
Surgical treatments may be necessary for severe herniated discs that do not respond to non-surgical treatments. These treatments include:
- Microdiscectomy: A microdiscectomy involves removing the portion of the herniated disc that is causing pressure on the spinal cord.
- Lumbar Laminectomy: A lumbar laminectomy involves removing a portion of the vertebrae to relieve pressure on the spinal cord.
- Spinal Fusion: Spinal fusion involves fusing two or more vertebrae together to stabilize the spine and reduce pressure on the spinal cord.
Benefits of Non-Surgical Herniated Disc Treatments
Non-surgical treatment options for herniated discs offer several benefits to patients. While surgery may be necessary for some cases, non-surgical treatment can be an effective option for mild to moderate cases.
One of the primary benefits of non-surgical treatment is that it is less invasive than surgery. Non-surgical treatments typically involve physical therapy, pain management, and lifestyle modifications. These treatments can improve the patient’s quality of life without the risks associated with surgery.
Non-surgical treatment options can also be more cost-effective than surgery. The cost of surgery can be high due to hospitalization, anesthesia, and other associated expenses. Non-surgical treatment options such as physical therapy or chiropractic care are often covered by insurance and can be more affordable for patients.
Another benefit of non-surgical treatment is that it can improve overall health and wellness. Lifestyle modifications such as regular exercise, healthy eating, and stress reduction can improve a patient’s overall health, which can in turn improve their spinal health.
While non-surgical treatment options can be a viable resource for many suffering with this condition there are times when surgery is the best option.
Factors that Determine If Surgery is Necessary
- Severity of symptoms: The severity of symptoms is a significant factor in determining whether surgery is necessary. If the herniated disc is causing severe pain, weakness, or numbness, surgery may be necessary. However, if the symptoms are mild, non-surgical options may be more appropriate.
- Location of the herniated disc: The location of the herniated disc is also an essential factor in determining whether surgery is necessary. If the herniated disc is pressing on a nerve root or the spinal cord, surgery may be necessary. However, if the herniated disc is not pressing on any vital structures, non-surgical options may be more appropriate.
- Age of the patient: Age can play a role in determining whether surgery is necessary. Younger patients may be more likely to recover from a herniated disc without surgery, while older patients may require surgery to alleviate their symptoms.
- Health conditions: Other health conditions may also play a role in determining whether surgery is necessary. For example, patients with diabetes or heart disease may be at higher risk for complications from surgery, and non-surgical options may be more appropriate.
Non-surgical treatments are often recommended for patients with mild to moderate herniated discs. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the best non-surgical treatment options for your specific case.
Risks and Complications of Lumbar Surgery
Lumbar surgery for a herniated disc carries certain risks and complications. Although it can be effective in relieving symptoms in severe cases, it is important to be aware of the potential risks and complications.
Some common risks associated with lumbar surgery for a herniated disc include bleeding, infection, nerve damage, and spinal fluid leakage. There is also a risk of complications related to anesthesia, such as allergic reactions and breathing difficulties.
In addition to the risks associated with surgery, there can be complications related to the healing process. These can include blood clots, fluid accumulation, and a slow recovery period. Some individuals may experience persistent pain, weakness, or numbness even after surgery.
It is important to discuss the potential risks and complications with your healthcare provider before deciding on lumbar surgery for a herniated disc. In some cases, non-surgical treatments may be effective in relieving symptoms without the risks and complications associated with surgery.
Can You Actually Avoid Surgery?
If you have a herniated disc, it is possible to avoid lumbar surgery in many cases. The severity of symptoms, the location of the herniated disc, the age of the patient, and the patient’s health conditions are all factors that determine whether surgery is necessary.
For mild to moderate cases, non-surgical treatments such as prp injections, prolotherapy, regenerative medicine, physical therapy, chiropractic care, pain management, and lifestyle modifications can be effective in reducing pain and improving spinal health. These treatments can be less invasive, more cost-effective, and have fewer risks associated with them than surgery.
However, in severe cases where nerve damage or spinal cord compression is present, surgery may be necessary. Surgical options may include discectomy, laminectomy, or spinal fusion. While surgery can be effective in relieving symptoms, it also comes with risks and a longer recovery period.
It is essential to seek medical advice if experiencing herniated disc symptoms. A healthcare professional can determine the best treatment options for your specific case, which may include non
Learn More About Alternative Ways to Alleviate Your Pain
Get back to doing the things you love, faster & without surgery.
Request an Appointment Today!