In the realm of regenerative medicine, few advancements hold as much promise and potential as the rejuvenation of damaged joints. From debilitating arthritis to sports injuries, the ability to regenerate and repair damaged joint tissue represents a transformative breakthrough in healthcare. Today, we delve into the fascinating world of regenerative medicine for joints, where science fiction is becoming a tangible reality.
The Science Behind Regenerative Medicine for Joints:
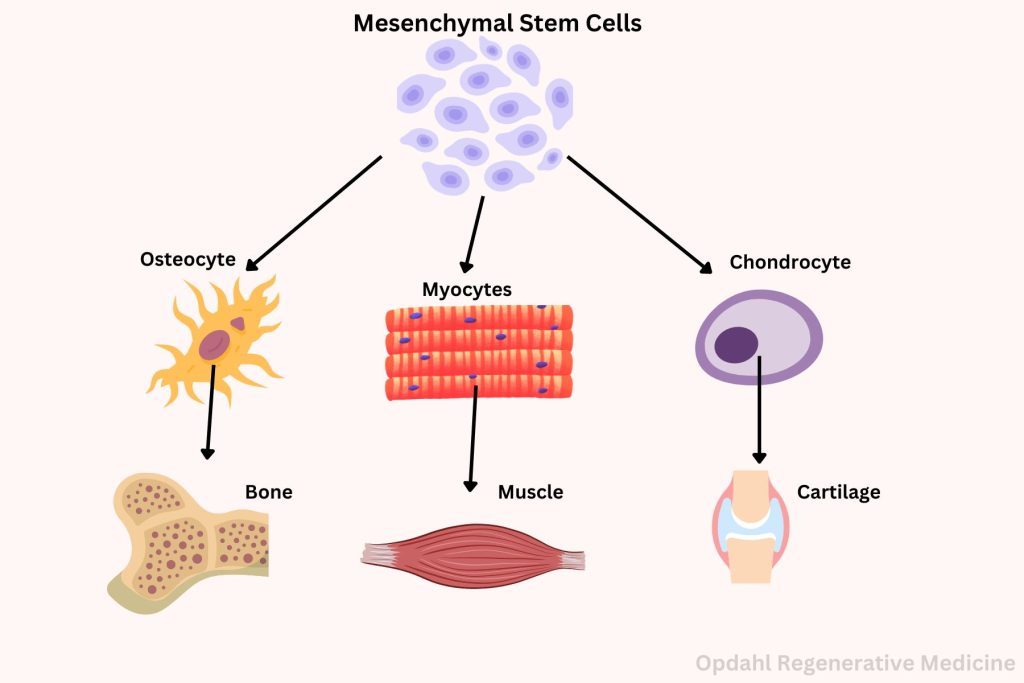
At the core of joint regeneration lies the remarkable capacity of the human body to heal itself. Unlike other tissues, such as nerves or muscles, joint tissue possesses a unique potential for repair and renewal. Stem cells, found abundantly within the body, play a crucial role in this process, serving as the building blocks for new cartilage, ligaments, and other essential components of healthy joints.
What is MFAT?
Mesenchymal Stem Cell Therapy (MFAT) is an innovative approach within regenerative medicine aimed at harnessing the transformative potential of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) for joint regeneration. These multipotent cells, typically sourced from bone marrow or adipose tissue, possess remarkable regenerative properties, making them ideal candidates for addressing the underlying causes of joint degeneration and injury. MFAT involves the isolation, concentration, and precise delivery of MSCs directly into the affected joint, where they initiate a cascade of regenerative processes. Through their ability to differentiate into various cell types, secrete bioactive factors, and modulate immune responses, MSCs promote tissue repair, reduce inflammation, and restore joint function. MFAT represents a personalized and minimally invasive approach to joint regeneration, offering new hope to individuals suffering from conditions like osteoarthritis, sports injuries, and other degenerative joint disorders.
The Marvel of Mesenchymal Stem Cell Therapy (MFAT):
While stem cell therapies have been a cornerstone of regenerative medicine for joints, recent advancements in the field have focused on the remarkable potential of Mesenchymal Stem Cell Therapy (MFAT). This innovative approach utilizes mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), a type of adult stem cell found in various tissues throughout the body, to facilitate tissue repair and reduce inflammation in damaged joints.
Harnessing the Power of MSCs:
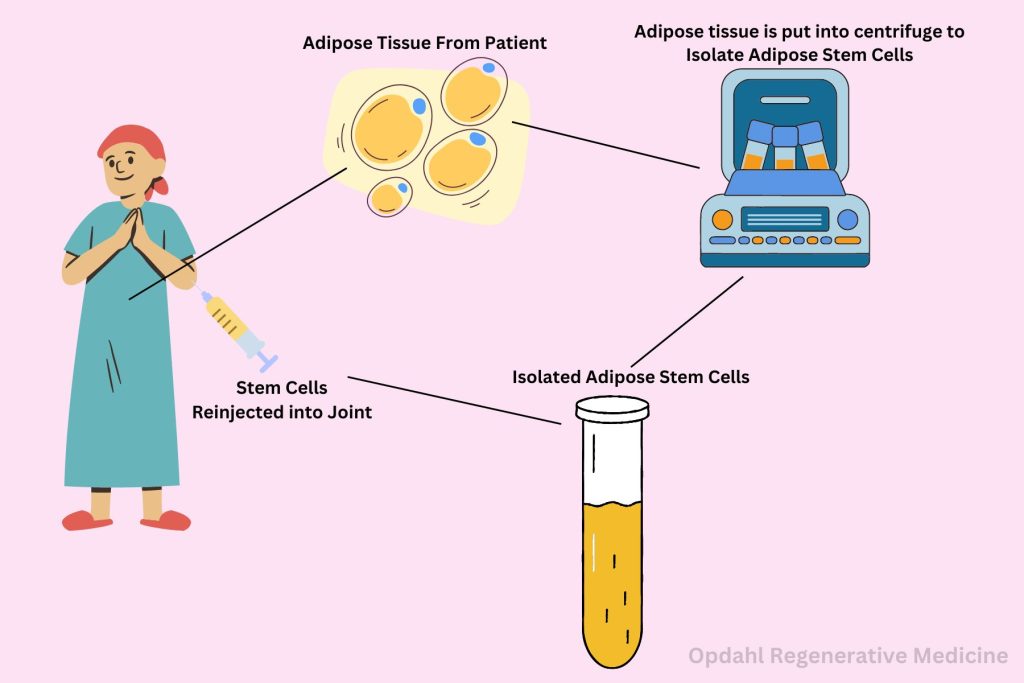
Mesenchymal stem cells are renowned for their ability to differentiate into a variety of cell types, including chondrocytes, the cells responsible for producing cartilage. This unique capability makes MSCs a potent tool in the regeneration of joint tissue. In MFAT, these cells are harvested from sources such as adipose tissue, then processed and concentrated before being injected directly into the affected joint. These multipotent cells, found abundantly within adipose tissue, possess remarkable regenerative capabilities that make them ideal candidates for addressing the complex challenges associated with joint degeneration and injury.
Promising Results of Regenerative Medicine:
Studies investigating the efficacy of MFAT have shown promising results in promoting joint repair and alleviating symptoms associated with conditions like osteoarthritis and sports injuries. By stimulating the body’s natural healing processes, MSCs not only facilitate the regeneration of damaged cartilage but also help reduce inflammation, pain, and stiffness in the joint.
MFAT Therapy Advantages:
Abundant and Accessible Source:
One of the key advantages of ADSCs (Adipose Derived Stem Cells) lies in their accessibility and abundance within the body. Adipose tissue, commonly known as fat, serves as a rich reservoir of stem cells. Adipose derived stem cells or ADSCs comprise a significant portion of its cellular composition. Harvesting ADSCs is a minimally invasive procedure that can be performed using techniques such as liposuction. This helps regenerative medicine clinics offer a readily available and renewable source of therapeutic cells for joint regeneration.
Versatility and Differentiation Potential:
ADSCs exhibit remarkable plasticity, with the ability to differentiate into various cell types, including chondrocytes, osteoblasts, and adipocytes. This versatility allows them to adapt and respond to the specific microenvironment of the joint. Once in the joints, they play a crucial role in promoting tissue repair and regeneration. By harnessing the regenerative potential of ADSCs, researchers can target the underlying mechanisms of joint degeneration. They can also address both the structural damage and inflammatory processes associated with conditions like osteoarthritis.
Immunomodulatory Properties:
Beyond their regenerative capacity, ADSCs possess potent immunomodulatory properties that make them particularly well-suited for applications in joint regeneration. Through the secretion of anti-inflammatory cytokines and growth factors, ADSCs can modulate the immune response within the joint environment. This dampens excessive inflammation and promotes a better environment for tissue repair. This immunomodulatory effect not only accelerates healing but also reduces the risk of adverse reactions. ADSC-based therapies are safe and well-tolerated by patients. In simple terms, immunomodulatory properties refer to the ability of certain substances, like stem cells, to affect the immune system in a way that helps the body fight diseases or reduce inflammation. These properties can either boost the immune system’s activity to fight off infections or suppress it when it’s overreacting, like in autoimmune diseases. Essentially, it’s like a smart regulator that helps keep the immune system balanced and functioning properly.
Clinical Applications and Efficacy:
Clinical studies investigating the efficacy of ADSC-based therapies for joint regeneration have yielded promising results. Many patients experienced significant improvements in pain relief, function, and quality of life. From intra-articular injections to tissue-engineered constructs, ADSCs offer versatile treatment modalities. These treatments can be tailored to the specific needs of each individual patient. Moreover, the safety profile of ADSC-based therapies has been well-documented. ADSC therapy is associated with minimal risks of rejection or adverse events reported in clinical trials. By utilizing a patient’s own stem cells, the risk of rejection or adverse reactions is minimized. This makes MFAT therapy a safe and viable option for a wide range of individuals. Additionally, the ability to tailor the treatment to each patient’s specific needs ensures optimal outcomes and enhanced long-term benefits.
Exploring Future Frontiers:
As research into MFAT continues to progress, scientists are exploring novel techniques to further enhance its therapeutic potential. Ongoing efforts aim to maximize the efficacy of MSC-based therapies for joint regeneration. Furthermore, advancements in tissue engineering and biomaterials offer exciting possibilities for creating scaffolds that support and guide the growth of new cartilage within the joint.
Seeking Professional Advice
In the realm of regenerative medicine, the potential for joint regeneration represents a beacon of hope for millions worldwide. What was once the realm of science fiction is now a tangible reality. As we continue to push the boundaries , the future looks bright for those in need of joint repair and rejuvenation. However, it is important to always consult with a qualified healthcare professional for personalized information and guidance.
Learn More About Alternative Ways to Alleviate Your Pain
Get back to doing the things you love, faster & without surgery.
Request an Appointment Today!
Sources:
Regenerative Medicine | Arthritis Foundation. (n.d.). https://www.arthritis.org/health-wellness/treatment/joint-surgery/preplanning/the-future-of-joint-repair